Osteochondrosis is a disease that can affect any person, regardless of gender and age. It manifests itself as pathological changes in the vertebral body, intervertebral discs and related structures (nerve roots, vascular plexuses and surrounding tissues).
Doctors identify a number of reasons leading to the development of osteochondrosis:
- prolonged stay in an uncomfortable position;
- lack of physical activity;
- violation of posture;
- excess weight;
- spinal injury;
- excessive physical activity;
- flat feet.
Osteochondrosis affects all parts of the spine, but it is the cervical region that is most vulnerable. This is due to the fact that the cervical spine takes on the main physical and functional load throughout the day, which leads to its overstrain. In addition, a large number of nerve endings are concentrated in the cervical region, which, in any unfavorable situation, make themselves felt. The vulnerability of this spine makes it an easy target for any kind of injury or stress.
Nervous experiences and physical stress create a strong muscle spasm, leading to compression of the neurovascular bundle, resulting in a violation of the blood supply to the intervertebral discs and the brain.
Osteochondrosis of the cervical spine symptoms
Osteochondrosis of the cervical spine manifests itself in a wide variety of clinical symptoms. The patient experiences paroxysmal pulsating headaches, which are more often localized in the occipital region. Disturbed by pain and stiffness in the neck and shoulders, weakness in the arms and a feeling of numbness in the fingertips appear. Often the patient feels a general malaise, rapid fatigability, even without intense physical exertion.
In the chronic course of the disease, an increase in blood pressure is observed, there is noise in the ears, flashing of flies in front of the eyes, and sleep is disturbed. In the absence of full-fledged medical care, the disease progresses, which further exacerbates the situation. Ischemia of soft tissues occurs, nerve roots degrade, intervertebral discs begin to collapse with the formation of intervertebral hernias.
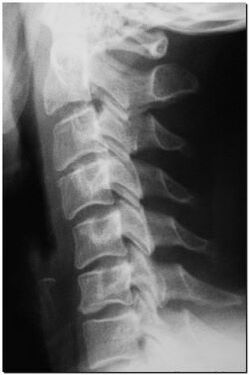
Diagnostics of the osteochondrosis of the cervical spine
In typical cases, in the presence of the above symptoms, the diagnosis of osteochondrosis of the cervical spine does not cause difficulties for doctors. But this conclusion requires additional neurological, orthopedic and X-ray examination. In the process of research, an anamnesis of the disease is collected, posture and range of motion in the spine are assessed, tension in the muscles of the back and points of soreness, limitation of mobility in the vertebrae are identified.
Treatment of osteochondrosis of the cervical spine
Treatment of cervical osteochondrosis requires a mandatory visit to a doctor. Therapy typically includes:
- Drug treatment - reduces inflammation;
- Manual therapy - relieves the patient from pain in the neck and relieves muscle tension;
- Therapeutic massage - improves blood circulation and metabolism in tissues;
- Exercise therapy (physiotherapy exercises) - strengthens the muscles of the neck, increases their tone;
- Physiotherapy procedures (electrophoresis, magnetotherapy, etc. ) - improves muscle nutrition;
- Implementation of recommendations for compliance with the regime of work and rest.
All of the above methods are quite effective, but a lasting therapeutic effect can be achieved only when they are combined. Therefore, the doctor draws up a rehabilitation program taking into account the individual characteristics of the course of the disease in each particular patient. In advanced cases, when the pain syndrome does not go away for a long time, and the listed methods do not provide relief, surgery is possible.
The diagnosis "osteochondrosis of the cervical spine" is not a sentence, but a reason to check the condition of our spine. Therefore, it must be remembered that osteochondrosis is a disease that is easier to prevent than to cure.